Whether it is sweltering summer time warmness or stifling site visitors, we ought to all use a blast of cool air now and then. It is where your car’s air con device comes into play. however have you ever been puzzled how exactly it cools matters down within the cabin?
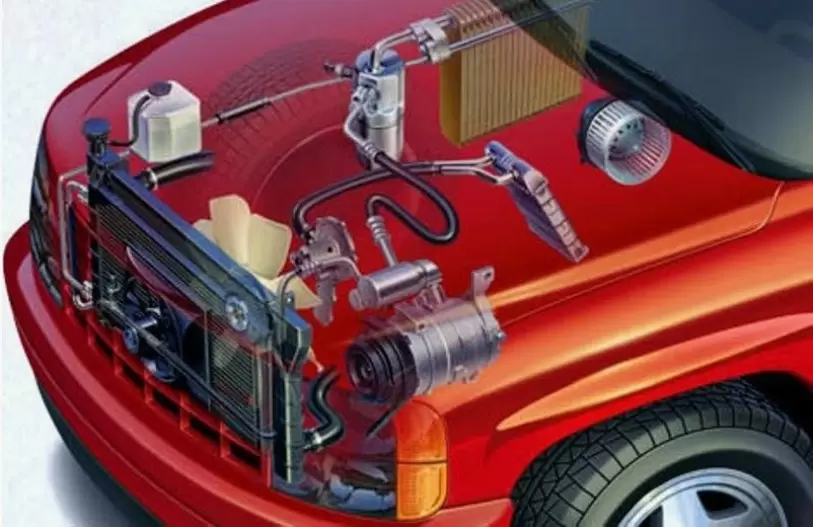
This in-intensity weblog publish will offer a pretty specific evaluation of every center issue that makes up an car’s a/c machine, explain how they work together step through step via lengthy descriptions and a couple of diagrams, and consist of visible a/c car diagrams to help illustrate the complicated cooling system.
By means of the end you may have professional level information of what’s absolutely taking place in the back of the dashboard to preserve you relaxed on warm days.
The Main Parts of an Automobile’s A/C System:
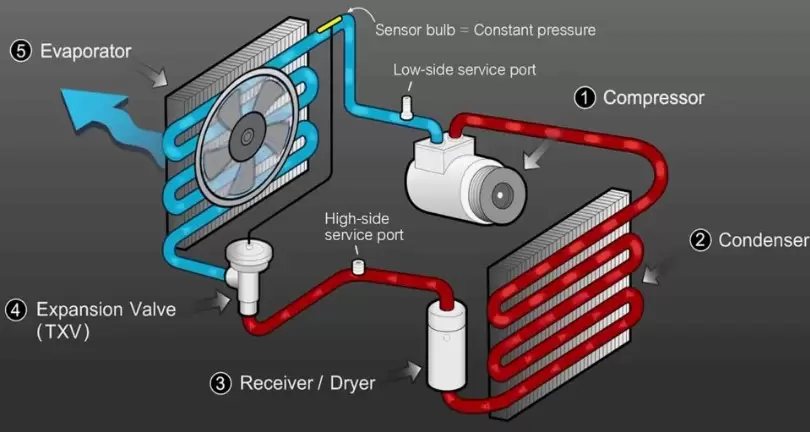
An a/c car diagram reveals there are five essential pieces that collaborate like a well-oiled machine to lower the air temperature inside your car.
Each one serves an important role in the carefully choreographed cooling cycle. Let’s examine what they are and delve deep into their functions.
The Compressor:
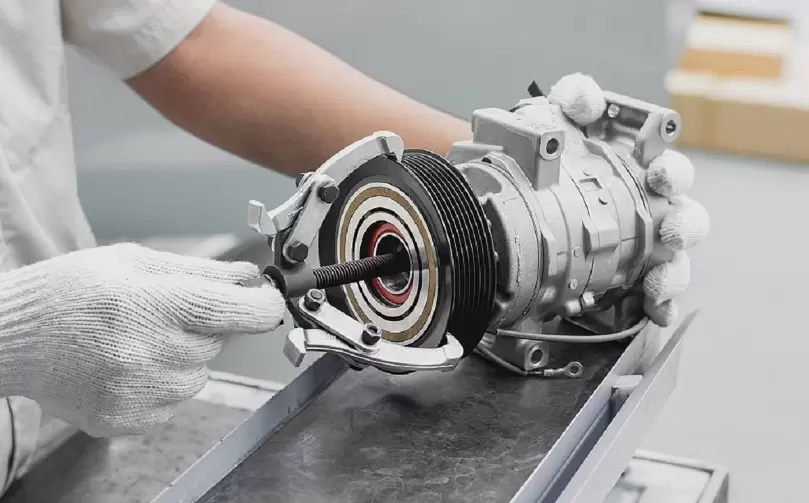

The compressor is the hearty heart of the a/c system. It works by compressing refrigerant vapor using precision-engineered pistons and pulling it into a higher pressure state through mechanical action.
This process requires substantial power, which is supplied by a durable engine belt connected to the car’s robust internal combustion engine.
The compressor itself is a rugged chamber housing pistons that shuttle back and forth. As the pistons retract, low pressure refrigerant vapor is drawn inside.
Then, as the pistons advance powerfully, they compress the vapor into a smaller, tighter space. This squeezing action exponentially increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. It’s then forcefully expelled towards the next link in the thermodynamic chain.
The Condenser:
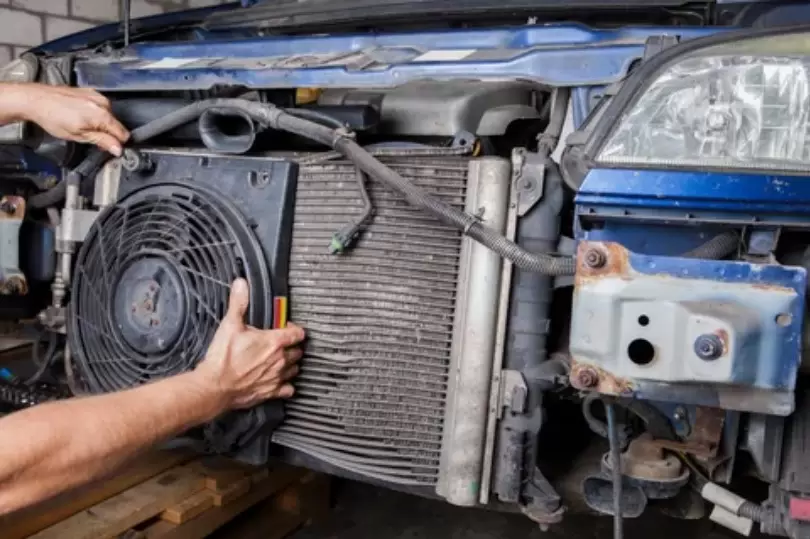

As the super-heated, high pressure refrigerant gas blasts out of the compressor chamber, it encounters the first heat exchange component: the condenser.
This part, usually located up front near the car’s nose cone, contains a complex array of ultra thin copper pipes ingeniously curled into tight coils and surrounded by closely packed aluminum fins.
As the scorching hot gas rushes through this finely tuned framework, the external fins’ broad surface area promotes efficient heat transfer.
Specifically, the fins release the gas’s excess thermal energy into the outgoing air flow generated by the vehicle’s robust fan system.
This causes the refrigerant’s temperature to plummet rapidly, transforming it from a searing vapor into a liquid state.
The condenser serves as a sophisticated cooling station, dissipating the heat and preparing the refrigerant for circulation’s next stage. Its technical design reflects advanced engineering aimed at maximizing the surface interface between the internal refrigerant and external airflow.
The Receiver Drier:

Now in its liquid form after exiting the condenser’s heat dumping domain, the refrigerant enters the receiver drier component more accurately known as the accumulator.
This part functions as the system’s filter, collecting any condensed moisture or debris.
Inside is a desiccant pack containing moisture absorbing agents designed to last the life of the vehicle. As liquid refrigerant permeates through the desiccant’s honeycomb structure.
it ensures any residual moisture is removed a critical task since even trace water levels can compromise performance over the long haul.
The receiver drier requires no maintenance, automatically isolating and soaking up impurities with each full-system circulation. Once fully dried and purified, the cooled refrigerant emerges spotlessly prepared for precise metering at the next station.
The Expansion Valve:
Upon leaving the receiver drier self cleansing chambers, the refrigerant encounters the delicate expansion valve. This minuscule device, smaller than a dime, wields immense responsibility for regulating refrigerant flow and precisely metering the amount entering the cold making evaporator component.
It does so via an automated needle containing a wax-like element that reacts to temperature. When the valve senses liquid refrigerant’s high temperature and pressure approaching from the condenser, its needle lifts open to allow gradual flow.
But as the refrigerant temperature drops on the other side within the evaporation chamber, the wax element contracts and the needle closes down – sustainably throttling flow to the necessary rate.
Without such an expansion valve performing this crucial flow control task, the evaporator would overload with too much hot liquid, inhibiting proper evaporation. Its functional sensitivity is critical for maximum cooling capacity.
The Evaporator:
It’s finally time for the main cooling event to commence as refrigerant reaches the evaporator component. Here is an expansive bundle of ultra thin copper tubing so infinitesimally small that hundreds of microscopic channels densely pack inside a space no bigger than a standard HVAC filter.
Coursing through this insanely complex capillary web is low-pressure gaseous refrigerant, having just undergone throttling and flash evaporation within the expansion device.
Inside the evaporator’s tubular maze, the tundra cold gas molecules make their final mission critical impact: to freeze air temperature upon contact.
As the frigid vapor circulates endlessly through the tubing network like an icy serpent, it absorbs massive heat from the surrounding cabin air forced over it externally by strategically placed inlet vents and the vehicle’s blower ventilation system.
This “steals” thermal energy from the air via heat transfer dynamics, lowering its temperature to the freezing zone desired by drivers and passengers alike.
The vapor then exits the evaporator replenished with absorbed heat, ready to return to the compressor and repeat its chilling role endlessly on the hottest of days, driven by the car’s reliable internal combustion heart.
Its function reduces temperatures inside the vehicle to comfortable levels that prevent heat stroke during long voyages.
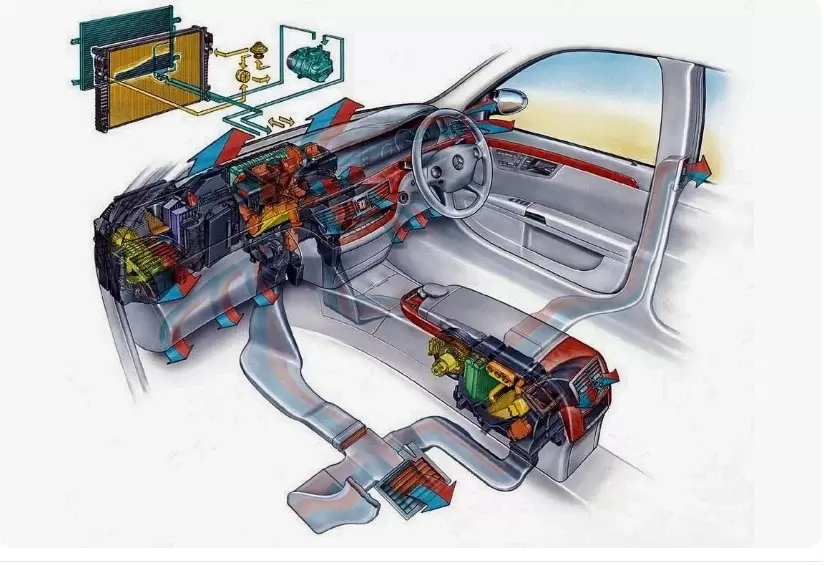
How an A/C System Works to Chill the Cabin Air:
Now that we have an in depth understanding of each individual component in granular technician-level detail, let’s pull back and examine the impressively synchronized larger-scale choreography playing out automotive wonders under the dash:
![A highly detailed labeled diagram of the a/c system components and complex refrigerant thermodynamic cycle]
As the diagram intricately portrays:
- Compressed refrigerant vapor exits the compressor as scorching hot high pressure gas, handing off its acquired thermal energy.
- Inside the condenser’s intricate coil and fin framework, the vapor swiftly loses its excess heat as it condenses into a liquid.
- This liquid collects in the receiver/drier’s purification chamber to shed contaminants before metering.
- It then undergoes controlled expansion within the needle valve, flash-evaporating into an ultra-low temperature mist.
- This frigid vapor enters the evaporator coil maze to commence its primary cooling task.
- Circulating through the evaporator’s microscopic passages, it absorbs immense warmth from the airstream.
- The cooled air is then forcefully distributed using vents and blower fans throughout the vehicle’s interior.
- Finally, the vapor departs the evaporator replenished with heat to repeat its chilling role, thus circulating endlessly to sustain comfort.
By analyzing each specialized process and heat transfer event in this grand thermodynamic circulation, one gains a true aerospace engineer’s grasp of automotive air conditioning fundamentals.
Understanding the bigger picture behind each minute detail enables more informed maintenance down the road.
Keeping Your A/C Operating at Peak Performance
To ensure this complex yet crucial system coined air conditioning continues providing dependable relief for many hot summer road trips ahead, do the following key maintenance tasks recommended by expert technicians:
- Check refrigerant charge levels every 30,000 miles using specialized gauges, and promptly refill low areas
- Closely inspect compressor operation using listening techniques and visible wear indicators
- Thoroughly examine condenser and evaporator coil condition for debris or signs of cracking
- Routinely replace cabin air filters contained in the blower housing every oil change
- Keep engine serpentine drive belt properly tensioned to avoid slippage wearing components
- Flush entire refrigerant circuit with approved cleaning chemical additives every 5 years
- Perform comprehensive leak checks under varying pressures using electronic sniffers
- Replace any deteriorated rubber or mechanical expansion valve components as needed
With diligent care and scheduled maintenance akin to this extensive overview, your air conditioning system’s performance should remain optimized for many summers of dependable comfort.
Feel empowered to better understand symptoms and complete basic repairs independently if issues arise down the road. A cold blast of cabin ventilation can make or break a hot ride now you know precisely how yours achieves that relief!

FAQ:
Q:What are the parts of AC for car?
A: compressor, condenser, evaporator, receiver-dryer, and an expansion tube.
Q:What is AC symbol in car?
A:snowflake ac symbol.
Q:How many parts does a car AC have?
A:five main components.
Q:How does car AC stop working?
A: most likely because of a freon leak or a bad compressor.
Q:What is inside part of AC?
A:Evaporator coils.
Conclusion:
In closing, we’ve delved deeply into the complex internal workings of an automobile’s air conditioning system. By breaking down each specialized component and understanding their coordinated interaction through in depth descriptions and detailed diagrams, you now possess an expert level grasp of the thermodynamic processes responsible for regulating cabin temperatures.
With this knowledge, minor issues need not leave you sweating on hot days. Applying periodic maintenance as recommended can extend your vehicle’s cooling capabilities for many seasons of comfortable travel. When hot weather strikes, you’ll truly appreciate the diligent efforts happening silently behind the dash.

With over 5 years of dedicated experience in the automotive industry, I am passionate about all things automotive. My journey began with a deep curiosity for automobiles, which led me to delve deeper into their mechanics, technology and trends. My expertise spans various aspects of the automotive world, from the latest electric vehicles to classic car restoration techniques. Through my articles, I aim to share my knowledge and insights, helping readers stay informed and inspired in the fast-paced world of the automobile.